Billions of birds are likely killed in the U.S. each year — but contrary to popular claims, wind turbines aren't nearly a primary culprit.
Former President Trump has continually used his prominent platform to claim that wind turbines — an economically sensible part of energy generation in the U.S. — are "killing our birds."
"The wind, it kills our birds. If you want to see a bird cemetery, go under a windmill sometime," Trump recently said on national TV, a clip that spread to the web. His running mate, JD Vance, snickered along during these repeated claims.
But in a sea of distorted facts, unvetted claims, viral falsehoods, and fake videos swirling through our internet existence, disseminating misinformation isn't too funny. Yes, as detailed below, wind farms do inevitably kill some birds — all energy production carries costs. But wind turbines, which are cleverly designed from airplane wings, are not what's decimating bird populations in the U.S.
"In comparison to wind farms, other aspects of human life are far more lethal, kill far more species, and are more problematic to fix," Anne B. Clark, a biologist and bird expert at Binghamton University, told Mashable.
Tweet may have been deleted
Tweet may have been deleted
What is killing U.S. birds
A host of human-caused factors kill birds. The most damaging, by far, live among us.
"The worst of these are feral or outdoor pet cats, estimated to kill as many as 4 billion birds per year, including many of the backyard songbirds that people value and control our insects," Clark explained. (At minimum, cats probably kill well over 1 billion birds in the U.S. annually.)
This is why biologists urge people to keep their cats inside. "Just one person keeping their cat indoors can save hundreds, maybe thousands, of birds. That’s a no-brainer," bird biologist Nico Arcilla previously told Mashable.
The next-highest bird killer in the U.S. are buildings (and their windows), estimated to kill some 365 to 988 million birds each year. "Those kills range from the tiniest hummingbirds to large owls," Clark said. (Here's how to limit the number of birds that crash into your windows.) And it's not just towering buildings. Any structures or objects in the path of bird flight — power lines, communication towers, and cars — contribute to the millions of avian deaths annually, Clark added. Cars kill an estimated 214 million birds each year.
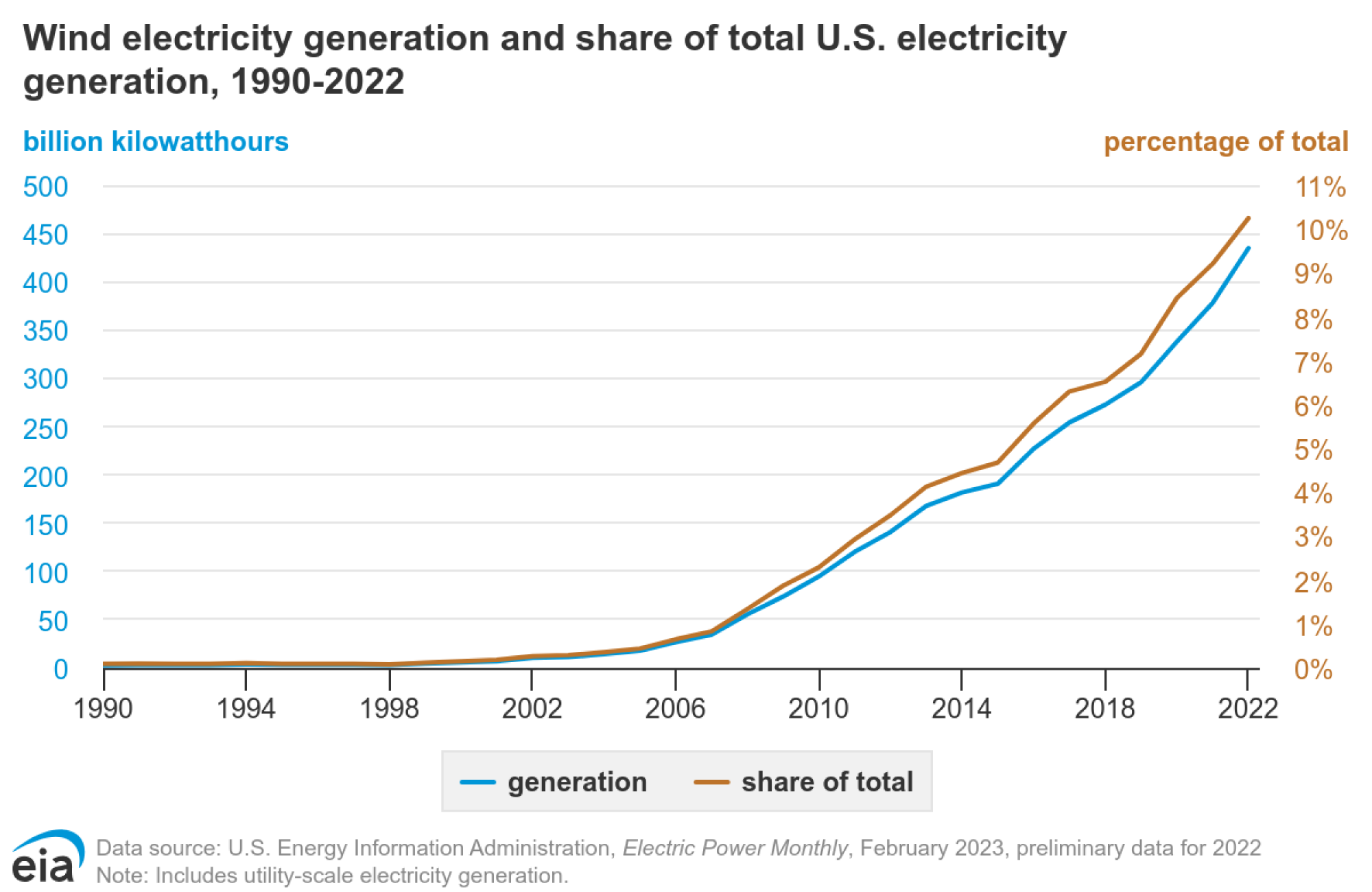
And then there are innumerable culprits that are difficult to count because they require collecting and assaying bird bodies for toxins. These include rodenticides, agricultural pesticides, water pollution, and beyond.
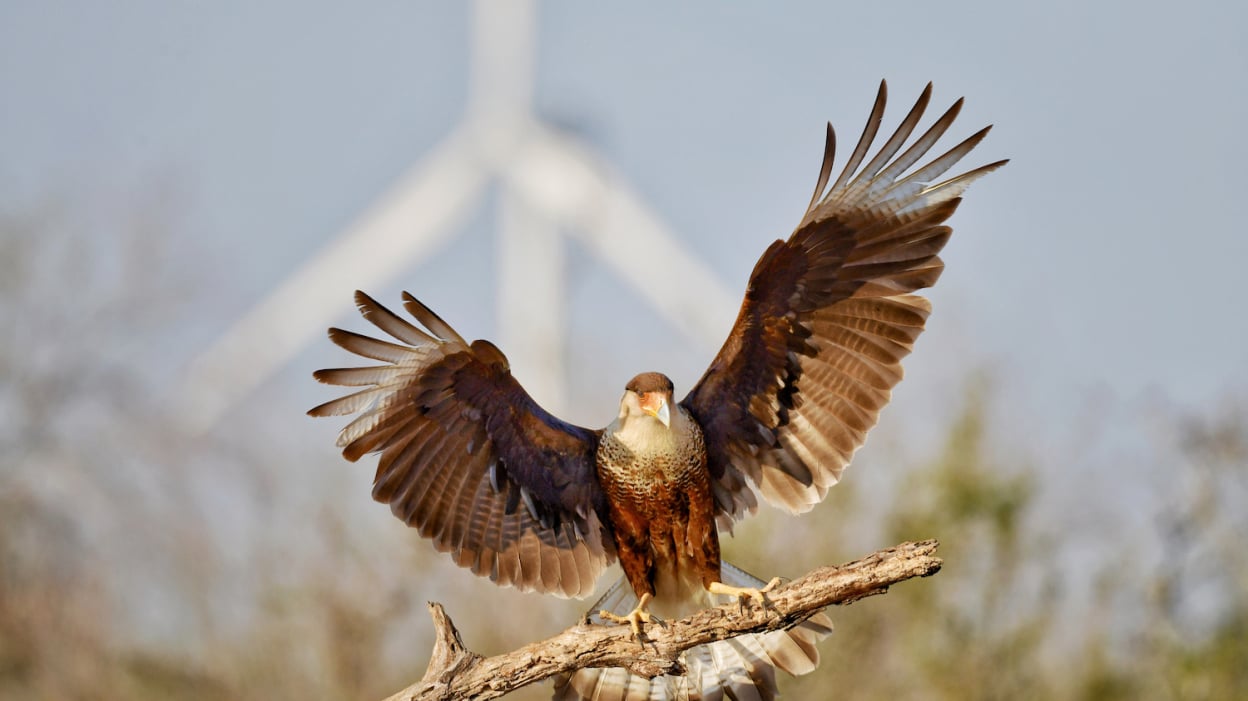
Wind turbines, however, are a relatively small player in bird mortality. "Research shows that wind projects rank near the bottom of the list of human-related bird mortalities, resulting in far fewer annual deaths than those caused by house cats, building collisions, or vehicle impacts," the Department of Energy explains. Turbines on land, with huge spinning blades, kill an estimated 234,012 birds annually, according to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
Wind farms limit bird deaths
Abundant wind energy, which supplies 125,000 jobs in the U.S. and cheap energy, is growing.
Fortunately, we can build or operate wind farms to curb avian deaths. "There are all sorts of ways that we can limit risks to birds," Jeff Buler, a wildlife ecologist at the University of Delaware, told Mashable.
This includes locating wind farms away from migratory passages, painting blades black (a visual aid that slashed bird deaths at a Norway wind farm by 70 percent), adding sound, and using fewer but larger turbines. Turbines can also be turned off on the handful of nights many birds are migrating through a specific region. Buler and other researchers found that by observing radar data, the migration of birds through corridors like the Great Lakes region can be well-predicted, allowing turbine operators the ability to temporarily shut down operations. "You can reduce collisions," Buler said.
"It's way easier to make false claims than back up claims with evidence."
While wind farms aren't free of environmental costs, they almost certainly kill far fewer birds than the fossil fuel sector, which requires intensive mining and burning of fuels.
"Coal-, oil-, and natural gas-fired power plants induce avian deaths at various points throughout their fuel cycle: upstream during coal mining, onsite collision and electrocution with operating plant equipment, and downstream poisoning and death caused by acid rain, mercury pollution, and climate change," according to a research article in the Journal of Integrative Environmental Sciences. The study concludes that "fossil-fueled facilities are about 35 times more dangerous to birds on a per GWh basis than wind energy." (A GWh, or Gigawatt hour, is a measurement unit for the production or consumption of energy.)
In the coming months and beyond, you're likely to see more misleading claims about renewable energy and a host of other topics. Beware the soundbites and spurious talking points.
"It's way easier to make false claims than back up claims with evidence," Buler said.
This story has been updated with more data about bird deaths in the U.S.
Topics Sustainability Donald Trump Nature